Download Files:
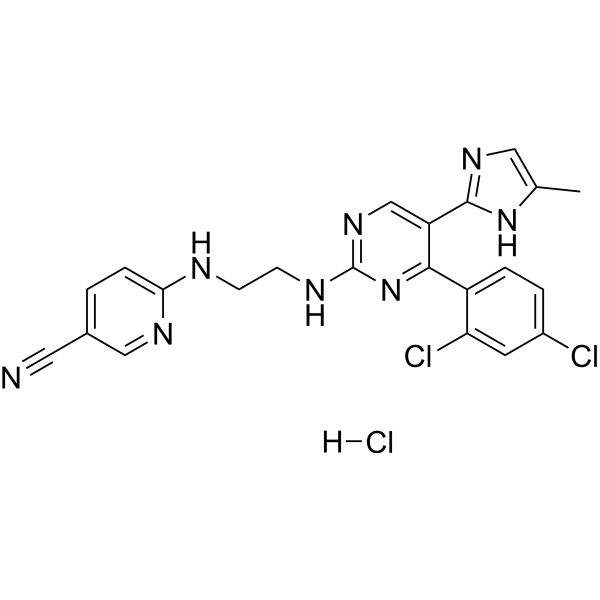
Laduviglusib (monohydrochloride)
SKU
HY-10182A-10 mg
Category Reference compound
Tags Autophagy;GSK-3;Wnt;β-catenin, Autophagy;PI3K/Akt/mTOR;Stem Cell/Wnt, Cancer
$88 – $605
Products Details
Product Description
– Laduviglusib (CHIR-99021) monohydrochloride is a potent and selective GSK-3α/β inhibitor with IC50s of 10 nM and 6.7 nM. Laduviglusib monohydrochloride shows >500-fold selectivity for GSK-3 over CDC2, ERK2 and other protein kinases. Laduviglusib monohydrochloride is also a potent Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway activator. Laduviglusib monohydrochloride enhances mouse and human embryonic stem cells self-renewal. Laduviglusib monohydrochloride induces autophagy[1][2][3].
Web ID
– HY-10182A
Storage Temperature
– 4°C (Powder, sealed storage, away from moisture)
Shipping
– Room Temperature
Applications
– Cancer-Kinase/protease
Molecular Formula
– C22H19Cl3N8
Citations
– Poult Sci. 8 March 2022, 101825.| Biochemistry and Cell Biology. Rice University. 2019 May.|ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018 Dec 19;9(12):3175-3185. |Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022 Sep;9(26):e2202505.|Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2023 May 1.|Ann Hematol. 2023 Sep 9.|Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jan 29;11(2):274.|Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Sep 5;503(2):1123-1129.|Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Apr 2;524(2):280-287.|Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 29 December 2021.|Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Jun 9, 10(6), 702.|Biomaterials. 2018 Oct;180:12-23.|Biomaterials. 2018 Dec 6;193:30-46.|bioRxiv. 2023 Aug 14.|bioRxiv. 2023 Jun 28.|Cancer Biol Med. 2020 Aug 15;17(3):707-725.|Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 3;13(5):1079.|Cell Biol Int. 2022 Sep 18.|Cell Death Differ. 2020 Jul;27(7):2158-2175. |Cell Death Dis. 2020 Mar 30;11(3):206.|Cell Death Dis. 2022 Mar 30;13(3):284.|Cell Death Discov. 2021 Oct 2;7(1):271.|Cell Discov. 2023 Jun 6;9(1):53.|Cell Prolif. 2021 Jan;54(1):e12932.|Cell Prolif. 2022 Mar 11;e13209.|Cell Prolif. 2023 May 5;e13498.|Cell Regen. 2020 Sep 3;9(1):15.|Cell Rep Med. 2020 Dec 22;1(9):100161.|Cell Rep. 2021 Nov 2;37(5):109949.|Cell Rep. 2022 Mar 29;38(13):110570.|Cell Reprogram. 2017 Dec;19(6):363-371.|Cell Signal. 2016 Mar;28(3):148-56. |Cell Signal. 2022 Nov 17;110526.|Cell Stem Cell. 2022 Jul 7;29(7):1102-1118.e8.|Cell Stem Cell. 2022 Sep 1;29(9):1366-1381.e9.|Cells & Development. 2021, 203665.|Chem Eng J. 1 January 2023, 138737.|Chemosphere. 2018 Oct 23;216:372-378. |Curr Biol. 2020 Nov 2;30(21):4128-4141.e5.|Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2018 Dec;81(1):e62.|Curr Res Neurobiol. 2023 Jun 17, 100095.|EMBO Rep. 2023 Jul 4;e57499.|Environ Toxicol. 2017 Oct;32(10):2316-2322.|Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021 Sep 10;106003.|Exp Cell Res. 2022 Nov 11;422(1):113416.|Exp Ther Med. 2020 Mar;19(3):1701-1710.|FASEB J. 2021 Jun;35(6):e21664.|Free Radic Biol Med. 2022 Jun 22;S0891-5849(22)00463-4.|Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 21;9:671704.|Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 20;9:712224.|Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 May 10.|Front Genet. 22 July 2022.|Front Med. 2021 Sep 23;8:746298.|Fundamental Research. 3 June 2022.|Harvard Medical School LINCS LIBRARY|Hepatology. 2022 Mar 27.|Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Jun 26;17(11):2683-2702.|Int J Biol Sci. 2023; 19(1): 204-224.|Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 12;23(16):9049.|Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23(14), 7586.|Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23(20), 12249.|Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 22;24(6):6008.|Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 31, 24(21), 15804.|iScience. 2023 Jul 21.|iScience. 6 October 2022, 105293.|J Biol Chem. 2022: 102703.|J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Jul;23(7):4627-4639.|J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Nov;25(22):10684-10697.|J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2021 Dec 8;271678X211065391.|J Exp Med. 2022 Nov 7;219(11):e20212405.|J Hazard Mater. 2023 Oct 5, 459, 132225.|J Int Med Res. 2021 Nov;49(11):3000605211055378.|JCI Insight. 2022 Jun 14;e158428.|Lab Invest. 2021 May 18.|Life Sci Alliance. 2022 Apr 19;5(8):e202201421.|Life Sci. 2020 Sep 1;256:117983.|Materials Today Chemistry 12 (2019) 78e84|Methods Mol Biol. 2022 Dec 15.|Mil Med Res. 2020 Sep 6;7(1):42. |Mol Cell. 2017 Mar 2;65(5):873-884.e8. |Mol Cell. 2022 Jun 3;S1097-2765(22)00480-4.|Mol Ther-Nucl Acids. 2021 May 28.|Molecules. 2020 Apr 23;25(8):1980.|Nat Chem Biol. 2020 Dec;16(12):1411-1419.|Nat Commun. 2022 Sep 6;13(1):5237.|Nat Med. 2016 May;22(5):547-56. |Nat Metab. 2023 Jun;5(6):1014-1028.|Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Nov 18;49(20):11575-11595.|Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Jul 1;gkac542.|Oncol Lett. 2023 Aug 30.|Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Nov 26;2020:4830418.|Patent. US20180263995A1.|Patent. US20210002607A1.|Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2023 Aug 9.|PLoS Biol. 2019 Oct 15;17(10):e3000498.|Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Mar 12;116(11):4989-4998.|Programa de Doctorado en Biomedicina. 2020 Sep.|Research Square Preprint. 2021 Feb.|Research Square Preprint. 2021 Nov.|Respir Res. 2022 Mar 25;23(1):70.|Rice University, Department of Biological Sciences. 2020 Apr.|Ruperto Carola University Heidelberg. Faculty of Natural Sciences and Mathematics. 03 Mar 2022.|Sci Adv. 2021 Apr 14;7(16):eabb2213.|Sci China Life Sci. 2018 Oct;61(10):1151-1167.|Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 10;9(1):18731. |Small. 2020 Jun;16(22):e2001371.|SSRN. 2023 Sep 1.|STAR Protoc. 17 June 2022, 101426.|STAR Protoc. 2021 Nov 5;2(4):100881.|STAR Protoc. 2023 Feb 3;4(1):102092.|STAR Protoc. 2023 Mar 16;4(2):102151.|Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Mar 29;12(1):214.|Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Feb 2;13(1):48.|Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Jan 5;14(1):1.|Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 Apr 16;11(1):157.|Stem Cells Int. 2018 Dec 25;2018:5965727.|Stem Cells Int. 2020 Feb 3;2020:8483035.|Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021 May;10(5):743-755.|Stem Cells. 2019 Apr;37(4):489-503.|Stem Cells. 2022 Jul 28;sxac050.|Theranostics. 2018 Jul 30;8(15):4262-4278.|Theranostics. 2019 Aug 12;9(20):5769-5783.|Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020 Jan 1;386:114813.|Toxicology. 2016 May 20;355-356:31-38. |Toxicology. 2020 Apr 15;435:152422.|Toxins. 2021 Aug 22;13(8):585.|University of Otago. Biomedical Sciences. 2021 Nov.|UNIVERSITY OF PAVIA. 2023 Jul 9.|Zool Res. 2021 May 18;42(3):377-388.|EMBO Mol Med. 2022 Nov 2;e16194.|J Transl Med. 2021 Oct 9;19(1):417.
References
– [1]Wang X, et al. Pharmacologically blocking p53-dependent apoptosis protects intestinal stem cells and mice from radiation. Sci Rep. 2015 Apr 10;5:8566.|[2]Bennett CN, et al. Regulation of Wnt signaling during adipogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2002 Aug 23;277(34):30998-1004.|[3]Ring DB, et al. Selective glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibitors potentiate insulin activation of glucose transport and utilization in vitro and in vivo. Diabetes. 2003 Mar;52(3):588-95.|[4]Naujok O, et al. Cytotoxicity and activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in mouse embryonic stem cells treated with four GSK3 inhibitors.BMC Res Notes. 2014 Apr 29;7:273.|[5]Ye S, et al. Pleiotropy of glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibition by CHIR99021 promotes self-renewal of embryonic stem cells from refractory mouse strains. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35892.
CAS Number
– 1797989-42-4
Molecular Weight
– 501.80
Compound Purity
– 99.93
SMILES
– N#CC1=CC=C(NCCNC2=NC=C(C3=NC=C(C)N3)C(C4=CC=C(Cl)C=C4Cl)=N2)N=C1.[H]Cl
Clinical Information
– No Development Reported
Research Area
– Cancer
Solubility
– DMSO : 60 mg/mL (ultrasonic)|H2O : 7.14 mg/mL (ultrasonic)
Target
– Autophagy;GSK-3;Wnt;β-catenin
Isoform
– GSK-3α;GSK-3β
Pathway
– Autophagy;PI3K/Akt/mTOR;Stem Cell/Wnt
Product type
– Reference compound
Disclaimer: All products are for Research use only unless clearly stated otherwise on the product datasheet. Datasheets provided on the website are drafts for reference purpose only and you are requested to always refer to the hard copy included in the kit for your experimentation. Agdia Products are available for delivery only in Canada.