Download Files:
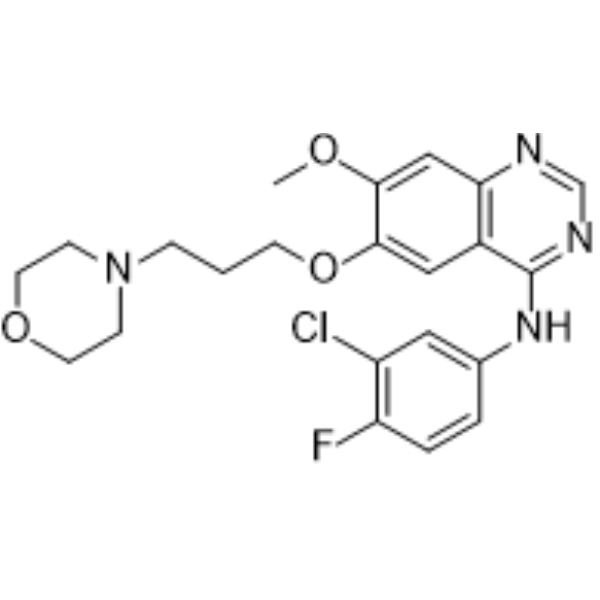
Gefitinib
SKU
HY-50895-1 g
Category Reference compound
Tags Apoptosis;Autophagy;EGFR, Apoptosis;Autophagy;JAK/STAT Signaling;Protein Tyrosine Kinase/RTK, Cancer
$60 – $180
Products Details
Product Description
– Gefitinib (ZD1839) is a potent, selective and orally active EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor with an IC50 of 33 nM. Gefitinib selectively inhibits EGF-stimulated tumor cell growth (IC50 of 54 nM) and that blocks EGF-stimulated EGFR autophosphorylation in tumor cells. Gefitinib also induces autophagy and cell apoptosis, which can be used for cancer related research, such as Lung cancer and breast cancer [1][2][5].
Web ID
– HY-50895
Storage Temperature
– -20°C, 3 years; 4°C, 2 years (Powder)
Shipping
– Room Temperature
Applications
– Cancer-Kinase/protease
Molecular Formula
– C22H24ClFN4O3
Citations
– AAPS PharmSciTech. 2022 Jan 4;23(1):48.|Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021 Jan;42(1):108-114.|Am J Transl Res. 2019 Jun 15;11(6):3543-3554.|Anticancer Res. 2020 Apr;40(4):1855-1866.|Aquaculture. 2021, 539: 736614.|Arch Toxicol. 2018 Jun;92(6):2027-2042.|Azhar Int J Pharm Med Sci. 2021;1 (1):66-72.|Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2023 Feb 11;166665.|Biomaterials. 16 September 2022.|Biomed Chromatogr. 2016 Jul;30(7):1150-4. |Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Sep;117:109185.|Biomed Res Int. 2020 Dec 24.|BMC Pulm Med. 2023 May 11;23(1):162.|Breast Cancer Res. 2017 Aug 4;19(1):90. |Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Dec 7;21(1):655.|Cancer Cell. 2018 Jun 11;33(6):1061-1077.e6. |Cancer Res Treat. 2023 Jan 26.|Cancer Res. 2023 Apr 16;CAN-22-3059.|Cell Death Dis. 2018 Feb 15;9(3):269. |Cell Death Dis. 2020 Nov 11;11(11):969.|Cell Death Dis. 2023 Oct 11;14(10):671.|Cell Death Dis. 2019 May 1;10(5):361. |Cell Death Discov. 2023 Nov 2;9(1):406.|Cell Insight. 16 June 2022, 100045.|Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 May;76(10):2015-2030.|Cell Oncol. 2021 Feb;44(1):109-133.|Cell Rep Med. 2023 Aug 25;101177.|Cell Rep Med. 2023 Jan 10;100911.|cell rep methods. 2023 Feb 27.|Cell Rep. 2019 Jul 9;28(2):512-525.e6. |Cell Res. 2020 Oct;30(10):833-853. |Cell Res. 2021 Jun;31(6):631-648.|Chem Biol Interact. 2022 Jan 5;109798.|Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2017 Aug 1;65(8):768-775.|Drug Dev Res. 2021 May;82(3):422-429.|EBioMedicine. 2022 Dec 14;87:104410.|Endocrinology. 2023 Mar 17;bqad042.|Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 30;910:174441.|Eur J Pharmacol. 2023 Oct 18:176114.|Exp Cell Res. 2017 Dec 15;361(2):246-256. |FEBS Lett. 2021 Sep 30.|Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020 Jul;102:211-217.|Food Nutr Res. 2018 Dec 6;62.|Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018 Mar 22;9:120. |Front Microbiol. 2022 Jun 30;13:894356.|Front Oncol. 2020 Dec 23;10:597434.|Front Oncol. 2020 Oct 5;10:542007.|Fundamental Research. 3 March 2022.|Haematologica. 2020 Jan;105(1):124-135. |Harvard Medical School LINCS LIBRARY|Infect Immun. 2021 May 24;IAI.00141-21.|Int J Biol Sci. 2021; 17(7):1671-1681.|Int J Med Sci. 2022 May 13;19(5):878-892.|Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 9;22(4):1745.|Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 4;23(3):1785.|Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23(5), 2664.|Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 15;19(10). pii: E3165. |Int J Oncol. 2022 Nov;61(5):139.|J Biol Chem. 19 September 2022, 102511.|J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020 Jul;146(7):1737-1749.|J Cell Mol Med. 2020 May;24(10):5578-5592.|J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Jan 24.|J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Jun 2.|J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 May 9, 116566.|J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Nov 29;37(1):295.|J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Mar 15;38(1):129. |J Exp Med. 2022 Jan 3;219(1):e20210789.|J Funct Foods. April 2022, 104997.|J Invest Dermatol. 2021 Aug 3;S0022-202X(21)01670-5.|J Sep Sci. 2017 Oct;40(19):3782-3791.|Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2023 Apr 14.|Lung Cancer. 2023 Jul;181:107258.|Mol Cancer Res. 2019 Feb;17(2):499-507. |Mol Med Rep. 2017 Sep;16(3):3475-3481.|Mol Pain. 2019 Jan-Dec;15:1744806919857297.|Mol Pharmacol. 2019 Dec;96(6):862-870.|Molecules. 2018 Mar 23;23(4). pii: E736.|Nat Biomed Eng. 2018 Aug;2(8):578-588.|Nat Commun. 2023 Apr 24;14(1):2342.|Nat Commun. 2023 Jun 15;14(1):3560.|Nat Commun. 2019 Apr 18;10(1):1812|Neurobiol Dis. 2020 Aug;142:104961.|Oncogene. 2018 Aug;37(31):4300-4312. |Oncogene. 2021 Jul;40(30):4884-4893.|Oncogene. 2021 Mar 9.|Oncol Lett. August 24, 2022.|Oncol Rep. 2018 Oct;40(4):2242-2250. |Oncol Rep. 2020 Aug;44(2):698-710.|Oncol Rep. 2023 May;49(5):84.|Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 13;6(31):31313-22. |Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 25;7(43):69760-69769.|Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 2;8(68):112313-112329.|Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023 Jan 31.|Pharmaceuticals. 2022, 15(6), 698.|Pharmacol Res. 2019 Jun;144:79-89. |Phytomedicine. 2023 May 16, 154884.|Research Square Preprint. 2023 Jun 15.|Research Square Preprint. 2023 May 4.|Research Square Print. December 9th, 2022.|Research Square Print. October 18th, 2022.|Sci Transl Med. 1 Sep 2021.|Sci Transl Med. 2018 Jul 18;10(450):eaaq1093.|Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2019 Dec 13;4:60. |SSRN. 31 Aug 2021.|Stem Cell Reports. 2017 Dec 12;9(6):1948-1960.|Theranostics. 2018 Jul 30;8(15):4262-4278.|Viruses. 2020 Aug 24;12(9):927.|Oncotarget. 2017 Oct 19;8(58):98771-98781.
References
– [1]Wakeling AE, et al. ZD1839: an orally active inhibitor of epidermal growth factor signaling with potential for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 2002 Oct 15;62(20):5749-54.|[2]Pedersen MW, et al. Differential response to gefitinib of cells expressing normal EGFR and the mutant EGFRvIII. Br J Cancer. 2005 Oct 17;93(8):915-23. |[3]Muhammad Tariq, et al. Gefitinib inhibits M2-like polarization of tumor-associated macrophages in Lewis lung cancer by targeting the STAT6 signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017 Nov;38(11):1501-1511. |[4]Mark S Cragg, et al. Gefitinib-induced killing of NSCLC cell lines expressing mutant EGFR requires BIM and can be enhanced by BH3 mimetics. PLoS Med. 2007 Oct;4(10):1681-89; discussion 1690. |[5]Tomoya Takenaka, et al. Effects of gefitinib treatment on cellular uptake of extracellular vesicles in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer cells. Int J Pharm. 2019 Dec 15;572:118762. |[6]Amin Li, et al. Gefitinib sensitization of cisplatin-resistant wild-type EGFR non-small cell lung cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020 Jul;146(7):1737-1749. |[7]Marie P Piechocki, et al. Gefitinib prevents cancer progression in mice expressing the activated rat HER2/neu. Int J Cancer. 2008 Apr 15;122(8):1722-9.
CAS Number
– 184475-35-2
Molecular Weight
– 446.90
Compound Purity
– 99.94
SMILES
– ClC1=C(C=CC(NC2=NC=NC3=C2C=C(C(OC)=C3)OCCCN4CCOCC4)=C1)F
Clinical Information
– Launched
Research Area
– Cancer
Solubility
– DMSO : 125 mg/mL (ultrasonic)
Target
– Apoptosis;Autophagy;EGFR
Isoform
– EGFR/ErbB1/HER1
Pathway
– Apoptosis;Autophagy;JAK/STAT Signaling;Protein Tyrosine Kinase/RTK
Product type
– Reference compound
Disclaimer: All products are for Research use only unless clearly stated otherwise on the product datasheet. Datasheets provided on the website are drafts for reference purpose only and you are requested to always refer to the hard copy included in the kit for your experimentation. Agdia Products are available for delivery only in Canada.